Abstract:
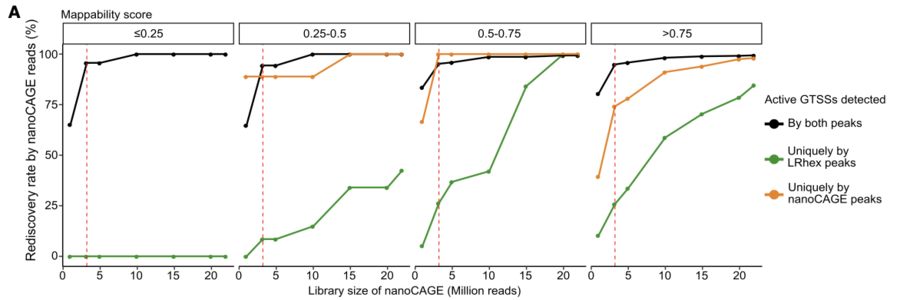
Recent studies have shown that the noncoding genome can produce unannotated proteins as antigens that induce immune response. One major source of this activity is the aberrant epigenetic reactivation of transposable elements (TEs). In tumors, TEs often provide cryptic or alternate promoters, which can generate transcripts that encode tumor-specific unannotated proteins. Thus, TE-derived transcripts (TE transcripts) have the potential to produce tumor-specific, but recurrent, antigens shared among many tumors. Identification of TE-derived tumor antigens holds the promise to improve cancer immunotherapy approaches; however, current genomics and computational tools are not optimized for their detection. Here we combined CAGE technology with full-length long-read transcriptome sequencing (long-read CAGE, or LRCAGE) and developed a suite of computational tools to significantly improve immunopeptidome detection by incorporating TE and other tumor transcripts into the proteome database. By applying our methods to human lung cancer cell line H1299 data, we show that long-read technology significantly improves mapping of promoters with low mappability scores and that LRCAGE guarantees accurate construction of uncharacterized 5′ transcript structure. Augmenting a reference proteome database with newly characterized transcripts enabled us to detect noncanonical antigens from HLA-pulldown LC-MS/MS data. Lastly, we show that epigenetic treatment increased the number of noncanonical antigens, particularly those encoded by TE transcripts, which might expand the pool of targetable antigens for cancers with low mutational burden.